Generative AI (GAI) is revolutionizing the business landscape, particularly in Human Resources and HR Technology. Its rapid adoption is unprecedented, with tools like ChatGPT, Stable Diffusion, and GitHub Copilot becoming integral to various business functions. GAI’s ability to create content from diverse data sets is particularly transformative for HR, enhancing productivity and offering insightful solutions to complex challenges.
The State of Generative AI in Business and HR
Based on a recent survey conducted by O’Reilly:
- ⅔ of survey participants indicated their organizations are working with GAI.
- A notable portion of AI adopters, about 26%, are newcomers, having engaged with AI for under twelve months, while 18% have already moved forward to implementing AI applications in active production.
- The primary challenge identified is the difficulty in pinpointing suitable real-world practical applications for available AI solutions.
- Open-source AI models are being utilised by 16% of AI tools users.
- Key areas of concern and testing among adopters include unexpected outcomes, security issues, safety, fairness and bias, and privacy considerations.
- A majority (54%) anticipate the primary benefit of AI being a substantial increase in efficiency, with only a small fraction (4%) expecting lay-offs.
Meanwhile, the McLean report indicates that only 28% of HR organizations are taking steps to implement generative AI. The reason cited is straightforward – a lack of time to delve into it.
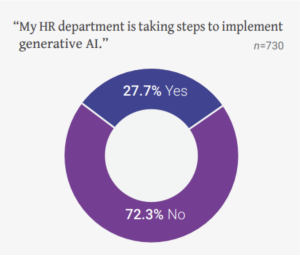
Source: HR Trends Report 2024, by McLean
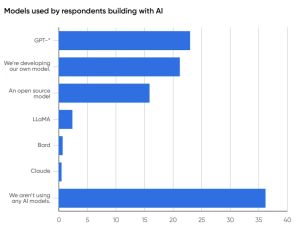
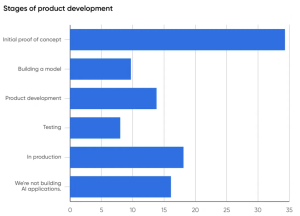
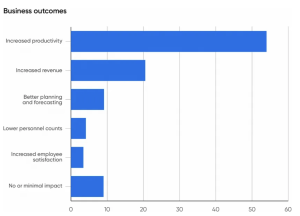
Source: O’Reilly
Use Cases of Leveraging Generative AI to Empower Business and HR
Generative AI in HR: A Paradigm Shift. HR’s engagement with GAI marks a strategic shift from traditional administrative roles to more dynamic, consultative functions. GAI aids in talent intelligence, employee experience, training, and compliance, as well as employee development and growth. This shift is not just about automating tasks but reimagining HR’s role in talent management, strategic planning, and organizational development.
Talent Intelligence and Recruitment. GAI is a game-changer in talent intelligence and recruitment. It enables HR professionals to source candidates intelligently, identify potential for promotion, and address pay inequities. Advanced AI tools can generate personalized job descriptions and candidate communications, significantly enhancing the recruitment process’s efficiency and effectiveness.
Enhancing Employee Experience. GAI-driven chatbots are revolutionizing employee experience by integrating documents, support materials, and transactional systems into user-friendly interfaces. These tools can significantly reduce the time spent on administrative tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Training and Compliance. The training and compliance sector is ripe for GAI integration. AI can generate training materials, create quizzes, and even act as a teaching assistant, transforming the way employees engage with learning and development programs.
Career Pathways and Employee Development. GAI is opening new avenues for employee development by providing career pathways based on AI analysis. This approach offers employees a clear vision of potential career trajectories, helping them make informed decisions about their professional growth.
Performance Management and Operational Improvement. In performance management, GAI can provide insights into team dynamics, skills composition, and other factors affecting performance. This data-driven approach enables HR to address performance issues more effectively and strategically.
Addressing Retention, Wellbeing, and Engagement. GAI can analyze data to identify factors contributing to turnover, employee burnout, and engagement issues. This capability allows HR to develop targeted strategies to improve employee retention and wellbeing.
Getting Started with Generative AI in HR. Implementing GAI in HR requires a strategic approach. It’s essential to identify specific problems to address, involve IT teams early in the process, and understand that AI systems require continuous tuning and maintenance. Starting small and scaling up as the system matures is a prudent approach.
The Future of HR with Generative AI. Generative AI is not a replacement for HR professionals but a tool that enhances their capabilities. As AI systems evolve, HR roles will shift towards more analytical, consultative, and design-oriented functions. This evolution will enable HR to play a more strategic role in organizational success.
Explore Boston Consulting Group’s perspective on the impact of Generative AI in HR in the image below.
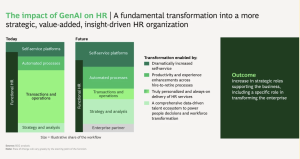
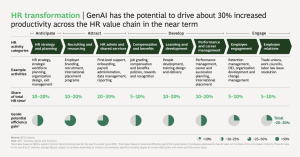
Source: BCG
Identifying Key Barriers and Risks in AI Adoption
- Challenges in Pinpointing Applications: A primary obstacle, noted by many, is the struggle to identify suitable business applications for AI. This issue underscores the necessity for more creative and strategic deployment of AI in business scenarios.
- Legal and Regulatory Hurdles: Concerns regarding legal matters, risks, and compliance are significant. The legal ramifications of employing generative AI, encompassing copyright issues and adherence to regulations, are still in flux and pose substantial concerns for enterprises.
- Absence of AI Governance Policy: The lack of a structured policy governing AI usage is a prominent concern, as indicated by 6.3% of adopters and 3.9% of non-adopters. Formulating and refining company policies for AI usage is essential to counter legal challenges and ensure regulatory adherence.
- Organizational Culture Resistance: An organizational culture that fails to acknowledge the necessity for AI presents an obstacle. This attitude may reflect a deficiency in innovative thinking or a hesitance to deviate from established business norms.
- Others (see the image below).
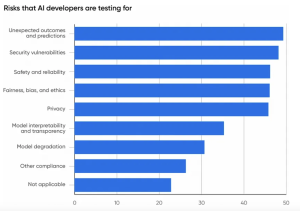
Source: O’Reilly
Missing Skills for utilizing AI potential
- AI Programming and Data Analytic Skills: Among AI users, 66% identify AI programming and 59% identify data analytic skills as the most needed ones. This highlights a skills gap in areas crucial for effective AI implementation and utilization.
- Shortage of Skilled Personnel: It is a concern for 9-13% of various groups of respondents. The demand for experienced AI developers and analysts is high, and finding the right talent is a challenge for many organizations.
- Infrastructure Challenges are also a barrier. Building and maintaining the proper AI tech infra basis is complex and pricy.
Conclusion
Generative AI is transforming HR from a traditionally administrative function to a strategic partner in business. Its impact on talent intelligence, employee experience, training, and performance management is profound. As businesses continue to adopt GAI, the role of HR will evolve, requiring a new set of skills and a strategic approach to harness the full potential of this transformative technology.


